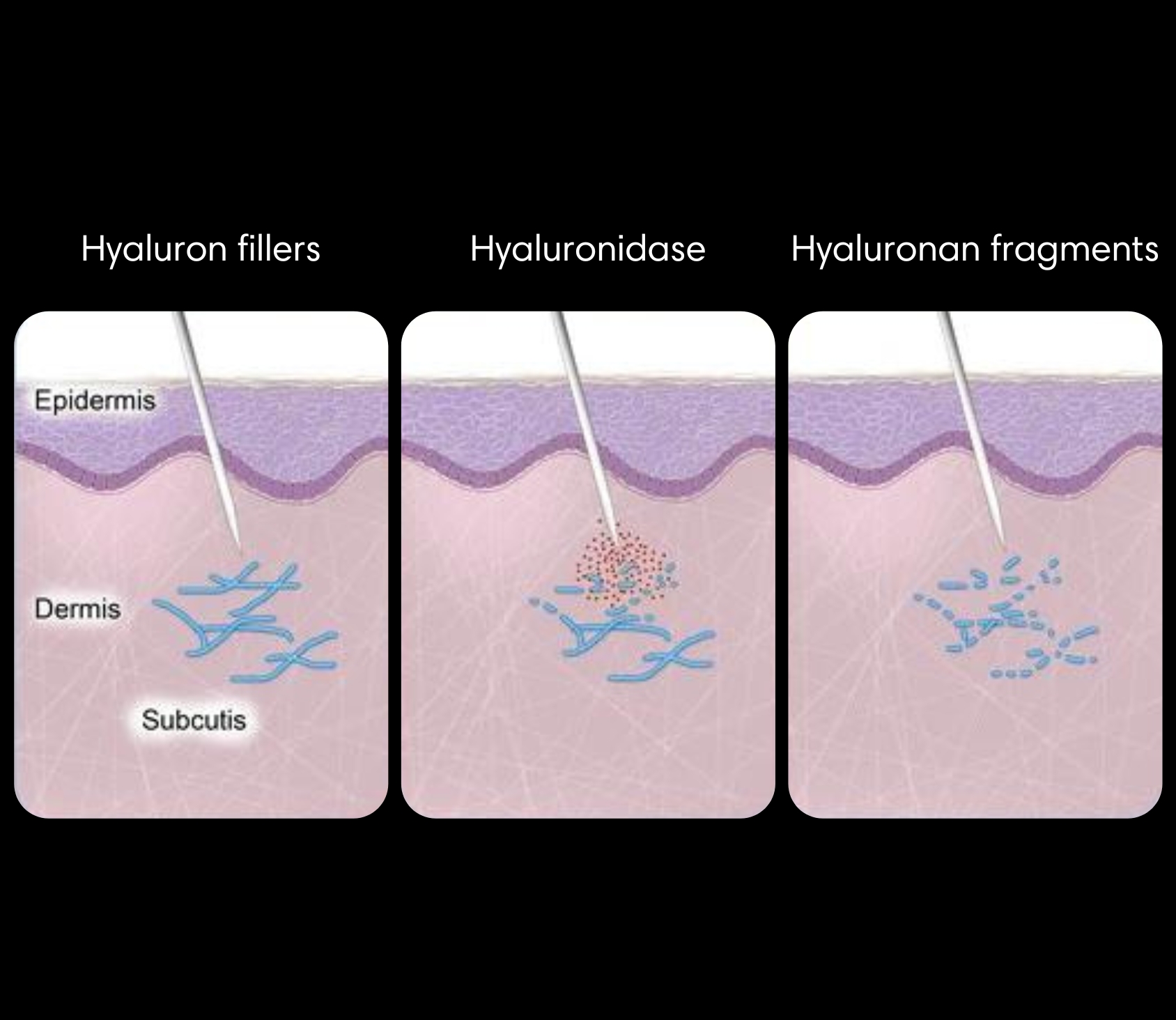
The most commonly used type of dermal filler is hyaluronic acid filler (HA). It’s the only dissolvable one, other types of fillers aren’t reversible.
Hyaluronidase is an enzyme that naturally occurs in our body, using it for filler dissolving, when it is injected into the filler area, it begins to break down the filler gel bonds.
It is used to adjust aesthetic outcomes, and treat any possible complications that might happen during or after dermal filler treatments.

The result can be noticed 24 hours to one week after, sometimes it may require multiple sessions to achieve adequate filler dissolving result.
There are many factors can affect the number of the sessions needed:
– If the filler is integrated into the tissues very well.
– Everyone’s body chemistry is different.
– Fillers brands have their own different composition.
– The amount of the injected filler.


There are many reasons to dissolve the filler:
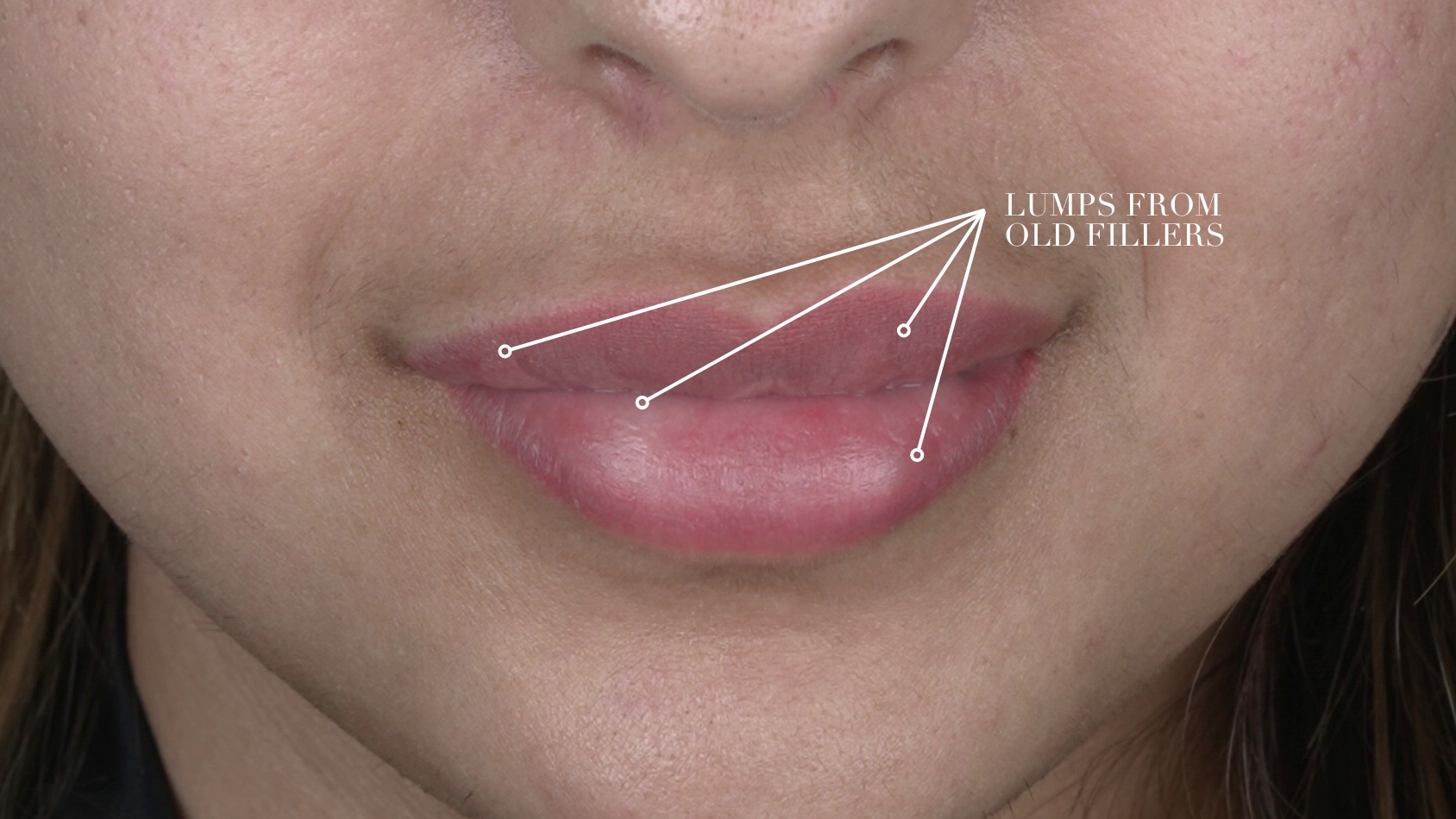
– In case of the Filler has been placed incorrectly or excessively, over-filling will affect the face contour and its appearance.
– Unevenness of the injected dermal filler will give an asymmetrical look result.
– The filler can be migrated, which means, moved or spread from the injected area to another.
– In case of any Lumps, pumps, and early or late nodular formation.
– People can have an Allergic reaction from the filler, although it’s rare, in this case, dissolving the filler helps in managing it.·In case any Infection happens from the filler injection, either done in a non-sterile way or for an unknown reason, dissolving the filler is one of the steps for managing those cases.
– Although it is rare, the most important indication to use the Hyaluronidase enzyme is hyaluronic acid-induced vascular occlusion. It’s a result of accidental injection of filler into an artery, or compression of the artery from surrounding filler which can rapidly progress to tissue necrosis, if not identified and treated quickly.
– Retinal branch artery occlusion is also a potential complication, caused by the retrograde arterial flow of the filler into the branches of the ophthalmic artery, which unfortunately can cause blindness.
The Injection sites at the highest risk of vascular occlusion are the glabella, nasal region, forehead, nasolabial fold, and periorbital area.
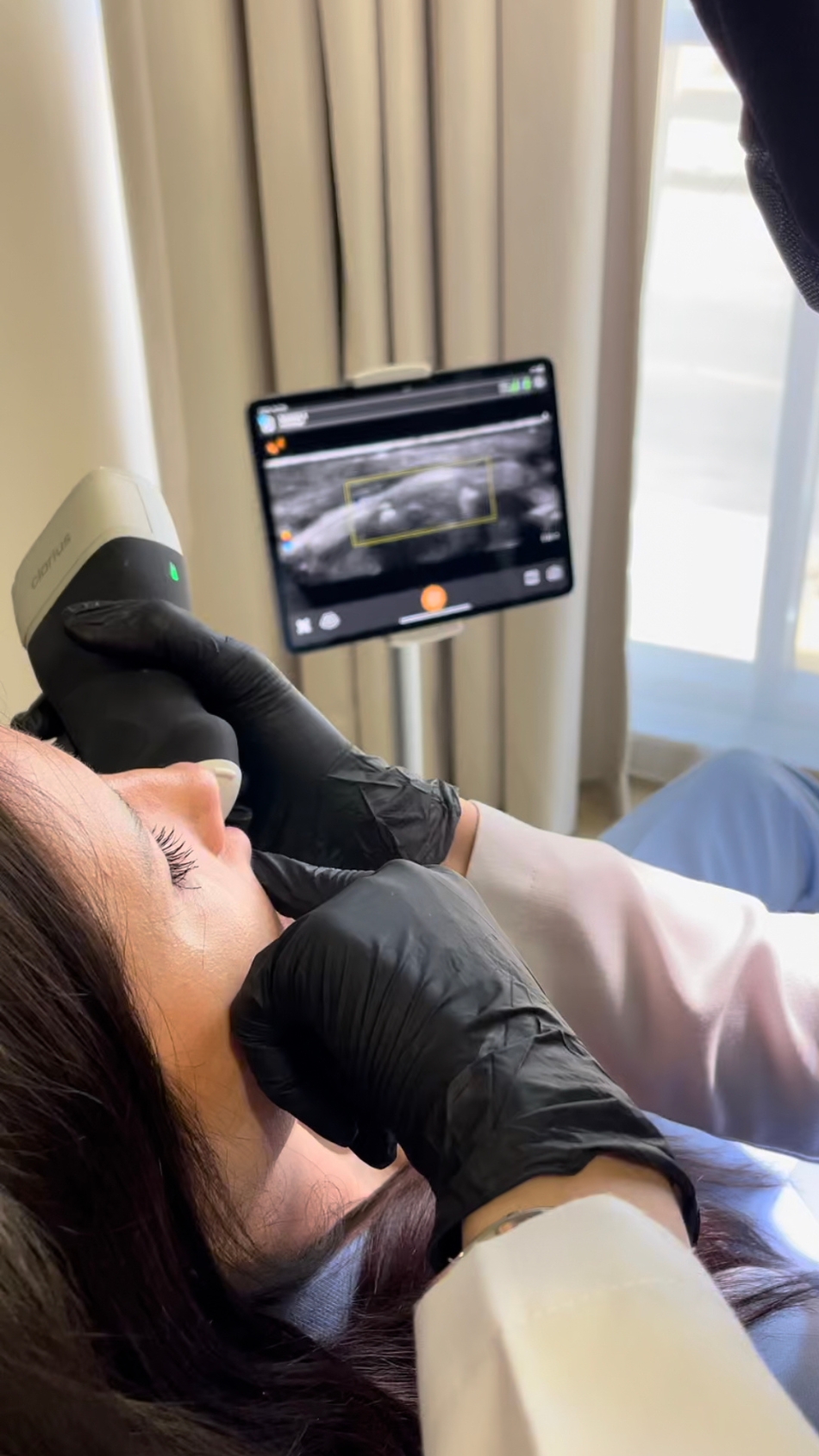

– Examination of the areas to determine where to dissolve. -Using ultrasound technology to allocate the filler or the nodule and guide where exactly the filler needs to be dissolved, using a minimal Hyaluronidase amount with minimal side effects.
– Explain the procedure, the risks, and after dissolving treatment instruction.
– As some people might have an allergic reaction, doing an allergic Patch test is very important. The test can be done by injecting a small amount of the enzyme into the arm skin and waiting for some time to see if there is any sign of allergy like swelling, itchiness, and redness at the injected site.
–Temporary swelling, tenderness and mild bruising in the treated area can be happen, those symptoms usually go away within 1 to 5 days.
-If the swelling is annoying, applying a cool compress for 15 minutes each hour helps in reducing the swelling.
Generally, there are no side effects, but potential risks to be considered. Hyaluronidase could potentially break down too much of the filler, as well as the body’s own HA (hyaluronic acid), the body will eventually produce more HA, but this can take a few months. To avoid this, use a minimal amount of the enzyme with multiple sessions if needed, rather than inject an unnecessary amount.
This article is Medically reviewed by : Dr. Iman Itani MBBS.GP. Aesthetic doctor.